 |
 |
- Search
| Intest Res > Volume 14(2); 2016 > Article |
|
Abstract
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is colonized by a dense community of commensal microorganisms referred to as the gut microbiota. The gut microbiota and the host have co-evolved, and they engage in a myriad of immunogenic and metabolic interactions. The gut microbiota contributes to the maintenance of host health. However, when healthy microbial structure is perturbed, a condition termed dysbiosis, the altered gut microbiota can trigger the development of various GI diseases including inflammatory bowel disease, colon cancer, celiac disease, and irritable bowel syndrome. There is a growing body of evidence suggesting that multiple intrinsic and extrinsic factors, such as genetic variations, diet, stress, and medication, can dramatically affect the balance of the gut microbiota. Therefore, these factors regulate the development and progression of GI diseases by inducing dysbiosis. Herein, we will review the recent advances in the field, focusing on the mechanisms through which intrinsic and extrinsic factors induce dysbiosis and the role a dysbiotic microbiota plays in the pathogenesis of GI diseases.
The gut microbiota fulfills an important role, helping to protect its host from disease.1,2 The gut microbiota inhibits the proliferation and colonization of pathogens by occupying potential intestinal niches and competing for nutrients.1,3 Additionally, the gut microbiota contributes to the differentiation and maturation of resident intestinal immune cells, including Th17 cells, regulatory T cells, innate lymphoid cells, and IgA-producing B cells.4 The gut microbiota also acts as a metabolic organ that interacts with host cells and provides the functional support required for the maintenance of homeostasis. For example, short chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are the end products of anaerobic bacterial fermentation of dietary fiber in the intestine, have been shown to enhance the epithelial cell barrier and anti-inflammatory immune cell function. Among these SCFAs, butyrate is important for the maintenance of various aspects of colonic homeostasis, such as intestinal motility, visceral blood flow, and suppression of pathogen expansion.5,6 Furthermore, the gut microbiota plays an essential role in the metabolism of bile acids. It has been established that the primary bile acids, cholic and chenodeoxycholic acid, are converted to more than 20 different secondary bile acid metabolites including deoxycholic acid (DCA) and lithocholic acid (LCA), by the gut microbiota.7 The accumulation of secondary bile acids, especially DCA, causes mucosal and DNA damage, leads to increased reactive oxygen species, and promotes tumor growth. In contrast, some secondary bile acids inhibit the growth of pathogens, suggesting that bile acid metabolism and its regulation by the gut microbiota can have both beneficial and harmful effects in the intestine.7
Under normal physiological conditions, the microbiota receives nutritional niches from the host. In turn, the microbiota provides symbiotic support for the host in the form of intestinal homeostasis maintenance. Thus, the host and its commensal microbes have a mutualistic relationship. However, some resident bacteria can acquire virulence, shift from symbionts to pathobionts, and contribute to the development and progression of various gastrointestinal (GI) diseases. A growing number of studies suggest that disturbance of the intestinal microbiota and its metabolic functions are strongly correlated with the initiation and progression of GI diseases, including functional dyspepsia, severe diarrhea, IBD, colorectal cancer (CRC), celiac disease, and IBS.8,9 It is now understood that disturbance of intestinal microbial communities, called dysbiosis, can be triggered by both extrinsic (e.g., diet, appendectomy, and antibiotic use) and intrinsic factors (e.g., genetics, stress, and aging). Here, we will review the pathogenic role of the gut microbiota in GI diseases.
IBD, comprising UC and CD, is chronic, relapsing inflammation of the GI tract. The development of IBD is governed by complex interactions between environmental risk factors, gut microbiota, and host genetics.10 Recently, the role of the gut microbiota in IBD pathogenesis has attracted considerable attention.11,12 It has been well documented that the diversity and richness of the gut microbiota are significantly reduced in patients with IBD, a condition referred to as dysbiosis.11,13 Moreover, the accumulation of certain pathobionts has been reported in both patients with IBD and animal models of IBD. This pathobiont accumulation may trigger, or at least contribute to, disease pathogenesis.1,12 For example, there is increasing evidence that defects in the inflammasome or NOD like receptor family pyrin domain containing protein (NLRP) signaling can lead to intestinal dysbiosis accompanied by an accumulation of potential pathobionts.14
Nlrp6-/- mice, which have impaired IL-18 production, are characterized by an abnormal expansion of the phyla Prevotellaceae and TM7. Prevotellaceae have the ability to enzymatically disrupt mucosal barrier function.15 Members of the phylum Prevotellaceae also tend to be more abundant in intestinal biopsy samples isolated from patients with IBD.16 Administration of dextran sodium sulfate (DSS), commonly used to trigger IBD-like experimental colitis in mice, induces significantly more severe inflammation in Nlrp6-/- mice than in wild-type mice.17 Nlrp6 deficiency leads to upregulation of CCL5; thereby promoting intestinal inflammation due to the recruitment of innate and adaptive immune cells.17 Notably, the colitogenic phenotypes observed in Nlrp6-/- mice are transmissible to wild-type mice upon co-housing with Nlrp6-/- mice.17 This suggests that the Nlrp6 deficiency in the host is not a requirement for the induction of colitogenic phenotypes; rather, dysbiosis driven by the Nlrp6 deficiency is the key factor responsible for triggering IBD-prone phenotypes in Nlrp6-/- mice.17 Likewise, mice deficient in Nod2, another gene known to be associated with CD susceptibility, also display alterations in their microbiota composition and increased susceptibility to DSS-induced colitis.18 The colitogenic phenotype of Nod2-/- mice, like that of Nlrp6-/- mice, can be acquired by wild-type mice through co-housing.18 However, unlike Nlrp6-/- mice, the bacterial strains that accumulate in Nod2-/- mice and drive this phenotype are unknown.
Mice deficient in IL-10 or IL-2 have also been used as a model of IBD-like spontaneous colitis. It is noteworthy that these animals either have no symptoms or develop only very mild colitis when housed under germ-free conditions, suggesting that the gut microbiota is a key driver of inflammation in these two models.19,20 Interestingly, some bacterial strains are capable of causing intestinal inflammation in these mice.21,22 For instance, monocolonization of germ-free Il10-/- or Il2-/- mice with a human commensal bacterium such as Escherichia coli or Enterococcus faecalis, results in intestinal inflammation, whereas monocolonization with another commensal bacterium Bacteroides vulgatus, does not. This type of intestinal inflammation is accompanied by increased production of two pro-inflammatory cytokines, IL-12 and IFN-γ Dual colonization of germ-free 129S6/SvEv Il10-/- mice by E. coli and E. faecalis induces more severe colitis than monocolonization does.23 In contrast, neither monocolonization nor dual colonization by these bacterial strains can induce the development of colitis in germ-free wild-type mice.21 Interestingly, colonization of germ-free HLA-B27 transgenic rats by B. vulgatus, but not E. coli, causes severe intestinal inflammation.24 These findings indicate that complicated interactions between commensal bacteria and the host's genetic background determine the fate of genetically susceptible individuals, i.e., colitis or no colitis.
In addition to genetics, other factors such as the environment can also trigger the development of IBD through dysbiosis. For example, dietary fats induce dysbiosis, thereby leading to intestinal inflammation.25 Devkota et al. demonstrated that taurocholic acid derived from dietary fats (milk-derived), but not from polyunsaturated fatty acids, promoted the expansion of a particular member of Deltaproteobacteria, a sulfate-reducing commensal bacterium Bilophila wadsworthia while reducing the abundance of Firmicutes. B. wadsworthia induced colitis in genetically susceptible IBD-prone Il10-/- mice,26 but not in wild-type mice, and the resulting colitis was mediated by more pronounced antigenspecific Th1 immune responses.27
B. wadsworthia produces hydrogen sulfate (H2S), a genotoxic chemical agent that is capable of causing inflammation. In this context, excessive protein ingestion raises the level of waste products in the colon, such as sulfates, nitrates, ammonium, and ethanolamine. These metabolites stimulate the overgrowth of sulfate-reducing bacteria such as Desulfovibrio spp. and Desulfuromonas spp.28 Notably, these bacteria are much more prevalent in patients with IBD than in healthy subjects.29 Given that the expansion of sulfate-reducing bacteria can also be induced by high dietary fats, it can be concluded that diet directly impacts mucosal immunity and IBD pathogenesis. Likewise, diets rich in fats and beef can induce the accumulation of potential pathobionts. The abundance of Erysipelotrichaceae and Bacteroides fragilis was significantly increased in subjects on diets rich in fat or beef.30,31 Although the pathogenic roles of these bacteria remain largely unknown, they were identified as potential pathobionts by IgA coating.32
In a recent study, Palm et al. demonstrated that the binding of IgA to intestinal bacteria can discriminate colitogenic bacteria from harmless non-colitogenic bacteria within the gut microbiota.32 IgA-binding intestinal bacteria induced more severe colitis when used to colonize germ-free mice after DSS administration.32 Notably, IgA-binding bacteria were present in both mice and humans (patients with IBD). Thus, although IgA identifies potential IBD-related pathobionts, dietary factors may regulate the abundance of these pathobionts in the intestine. These findings support the notion that the typical western diet may promote alternations in the composition of the microbiota, resulting in an accumulation of colitogenic pathobionts, and perturbed colitogenic microbiota facilitates the development and/or progression of IBD. Smoking is a well-known environmental factor that exacerbates IBD symptoms.33,34
A meta-analysis showed that Anaerostipes, which convert lactate to butyrate, were lower in patients with IBD who smoked than in those that did not.35 Thus, smoking may lead to decreased butyrate production by the microbiota. Given that butyrate contributes to intestinal homeostasis by enhancing epithelial barrier function and facilitating regulatory T cell development,5,6 impaired butyrate production due to smoking may increase the susceptibility of the host to IBD.
Antibiotic treatment is one of the most potent factors that can lead to a disturbance in healthy intestinal microbiota. Studies have shown that administration of antibiotics in the first year of life is associated with the development of pediatric IBD.36,37 Patients with IBD who were treated with ciprofloxacin and metronidazole had a reduced abundance of Dorea, Butyricicoccus, and Coriobacteriaceae.36,37 Organic compounds produced by these bacteria, such as formate and butyrate, are important for the regulation of gut homeostasis. Additionally, gut dysbiosis driven by antibiotic use often results in the overgrowth of pathogens. For instance, the abundance of Clostridium difficile is effectively suppressed in a healthy intestine by other commensal microorganisms. However, once the healthy microbial community is disrupted by antibiotics, C. difficile can bloom in the gut and cause C. difficile-induced colitis.38,39
C. difficile infection causes significant morbidity and mortality in hospitalized patients40 and is a serious complication for patients with IBD. Although the precise mechanism is unclear, IBD is a risk factor for C. difficile infection.41,42 Moreover, C. difficile infection also exacerbates IBD.42,43
A key mechanism by which gut dysbiosis increases susceptibility to C. difficile infection is perturbation of the luminal metabolic profile. It has been well documented that antibiotics significantly decrease the abundance of bacteria responsible for bile acid metabolism.44 Given that these bacteria can convert primary bile acids into secondary bile acids, the ratio of primary to secondary bile acids is significantly increased after antibiotic treatment.45 Primary bile acids are known to promote the growth of C. difficile, whereas secondary bile acids inhibit C. difficile growth.45,46
Buffie et al. recently identified Clostridium scindens as a key bacterium that suppresses the growth of C. difficile.47
C. scindens has high levels of bile acid 7alpha-dehydroxylating activity, which converts primary bile acids to secondary bile acids. Interestingly, the abundance of C. scindens is significantly reduced in C. difficile-susceptible mice and humans.47 Additionally, adoptive transfer of C. scindens into C. difficile-susceptible (antibiotic-treated) mice inhibited the germination of C. difficile spores via DCA production.47 As it has been reported that the balance of primary and secondary bile acids in the intestine is perturbed in patients with IBD,48,49 this dysbiosis-induced imbalance of microbial metabolites may be associated with the increased susceptibility to C. difficile of patients with IBD. Further studies focusing on the luminal metabolites produced by dysbiotic microbiota are needed to unravel the precise mechanisms involved in the increased susceptibility of patients with IBD to C. difficile colonization.
In addition to pathogen overgrowth, dysbiosis in IBD can also result in the loss of beneficial commensal bacteria, increasing the risk of intestinal inflammation. For instance, a lower abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is associated with a higher risk of postoperative recurrence of inflammation in patients with IBD, particularly CD patients.50,51
F. prausnitzii is one of the most abundant anaerobic bacteria in the human gut. It has an important function, providing energy to colonocytes and maintaining overall intestinal health. There is also evidence that F. prausnitzii has strong anti-inflammatory effects. These effects are mediated by the induction of a tolerogenic cytokine profile, which includes lower IL-12 and IFN-γ production and elevated levels of IL-10.51 Notably, in a mouse model of intestinal inflammation, oral administration of F. prausnitzii showed anti-inflammatory effects and ameliorated colitis.51 These results indicate that F. prausnitzii can counterbalance dysbiosis and may be a promising candidate probiotic for the treatment of CD. What is still unclear is the cause of the reduced abundance of F. prausnitzii in patients with IBD. Further studies are needed to determine whether this approach can be translated into novel and effective IBD treatment options.
CRC is a common cancer, causing about 500,000 deaths worldwide every year. The incidence of CRC is higher in the western world,52 and this increased incidence is largely due to the dietary differences between developed and developing countries. Recent meta-analyses indicate that diets rich in fiber are associated with a lower risk of CRC,53 whereas consumption of saturated fat-rich foods such as red and processed meat, is strongly associated with an increased risk of CRC.54,55 An epidemiological study showed that the incidence of CRC in African Americans who generally consume high-fat, low-fiber diets was higher than that of rural indigenous Africans who generally consume low-fat, high-fiber diets.56 In addition, there were significant differences in the microbiota composition and the metabolic profiles of these two groups; fecal samples from African Americans had lower numbers of total bacteria and the major butyrate-producing groups and higher numbers of hydrogen sulfide-producing bacteria than fecal samples from indigenous Africans. Additionally, the fecal concentrations of secondary bile acids such as LCA and DCA, were higher in African Americans, whereas the concentrations of SCFAs such as acetate, butyrate, and propionate, were higher in indigenous Africans.56
In fact, previous reports on dietary fat consumption and CRC risk have shown that secondary bile acids are increased and SCFAs are decreased in patients with CRC.57,58 Similarly, consumption of diets rich in beef also affects the composition of the intestinal microbiota. The abundance of B. fragilis was significantly higher in individuals consuming a diet rich in beef than in those consuming a vegetarian diet.31 The enterotoxigenic form of B. fragilis, enterotoxigenic B. fragilis (ETBF), is associated with acute diarrheal disease, IBD (as discussed above), and CRC due to production of the B. fragilis toxin.59
B. fragilis toxin alters the structure and function of colonic epithelial cells, and cleaves the tumor suppressor protein E-cadherin, which is critical for the formation and maintenance of adherent junctions in areas of epithelial cell-cell contact. The toxin increases the permeability of the epithelial barrier and enhances Wnt/β-catenin signaling, resulting in an increased colonic carcinoma cell population.60
Importantly, colonization by ETBF, but not non-toxigenic B. fragilis, promotes colonic colitis and carcinogenesis in CRC model MinAPC716 +/- mice.61 This finding indicates that in MinAPC716 +/- mice, ETBF specifically activates STAT3, a key regulator of CRC development, by increasing IL-17 production by Th17 cells in the colonic tissue. Blocking IL-17 or IL-23R can significantly reduce tumor formation in vivo.61 ETBF tends to be more abundant in patients with CRC than in healthy individuals.62 Genotoxins also have a considerable effect on the composition of microbial communities and can promote tumorigenesis. The adherent-invasive E. coli strain NC101 induces DNA double-strand breaks by utilizing several of the enzymes involved in the production of colibactin, which are encoded on the polyketide synthase (pks) genotoxic island.63 Although monocolonization of azoxymethanetreated germ-free Il10-/- mice by E. coli NC101 promoted tumor formation and intestinal inflammation, monocolonization of these mice by a pks-deleted mutant showed significantly reduced tumor multiplicity and invasion.64 However, colonization of azoxymethane-treated wild-type germ-free mice by E. coli NC101 does not result in tumor development, suggesting that bacteria-driven inflammation is required for carcinogenesis mediated by this bacterium.64 It is noteworthy that pks+ E. coli tend to be more abundant in patients with IBD or CRC than in patents without IBD and CRC.64
High consumption of alcohol also increases the risk of CRC.65 A higher incidence of CRC was observed in heavy drinkers than in non-drinkers, and the microbial composition in the gut of these two groups was different.66 Mutlu et al. showed that intestinal dysbiosis is observed in persons with alcoholism. In particular, the abundance of Bacteroidetes is lower and the abundance of Proteobacteria is higher in people with alcoholism than in healthy controls.67 Interestingly, the abundance of gram-positive Erysipelotrichaceae, which are considered to be pro-inflammatory (as described above), was higher in chronic alcohol-fed mice than in control mice.68 This observation also holds true in CRC patients.69 Expression of REG3γ, an antimicrobial peptide that targets gram-positive bacteria, was downregulated in alcohol-fed mice. This result suggests that alcohol consumption leads to an overgrowth of Erysipelotrichaceae due to lower REG3γ expression. Collectively, these findings support the notion that excess alcohol consumption leads to the development of CRC through dysbiosis, although the underlying mechanism remains unclear.
The aging process also plays a key role in CRC pathogenesis, and aging has been shown to affect the composition of the human microbiota. Studies of the relationship between age and microbiota composition have demonstrated that both the total number of bacteria and bacterial diversity decrease with age. In fact, a lower abundance of Firmicutes and a higher abundance of Bacteroidetes were observed in older populations.70,71 There is also evidence that older age is associated with decreased butyrate production and reduced numbers of F. prausnitzii and Roseburia intestinalis,72 antiinflammatory bacteria with protective roles against CRC.73 Thus, the aging process may affect gut homeostasis, thereby increasing the risk of CRC development.
Bacteria of the genus Fusobacterium are oral commensal organisms that maintain epithelial barrier function by producing butyrate.74 However, these bacteria have pathogenic potential in the gut. For example, an invasive strain of Fusobacterium nucleatum has been shown to promote the onset of colonic tumorigenesis by mediating E-cadherin/β-catenin signaling via an adhesion protein called FadA.75
F. nucleatum has also been shown to be highly prevalent in the intestinal tissue and stool of patients with CRC.76 These findings suggest that although F. nucleatum is a beneficial commensal bacterium, its abnormal accumulation may increase the risk of CRC.
All of these findings suggest that changes in the structure, distribution, and metabolism of the colonic microbiota, which can be triggered by diverse factors, may contribute to the development and progression of CRC. A better understanding of the mechanisms that influence homeostasis of the gut microbiota will pave the way for novel and effective approaches to prevent and treat CRC (Table 1 and Fig. 1).
Celiac disease, a chronic immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the small intestine, is an autoimmune disorder triggered by the consumption of dietary gluten.77 Studies suggest that alterations in the gut microbiota composition may contribute to the development and/or progression of celiac disease.78 Changes in the intestinal metabolic profile, including alterations in SCFA production, have also been reported in patients with celiac disease.79 It has been reported that Klebsiella oxytoca, Staphylococcus epidermidis, and Staphylococcus pasteuri are more abundant in duodenal biopsy specimens from patients with active celiac disease than in specimens from healthy individuals. In contrast, Streptococcus anginosus and Streptococcus mutans are less abundant in patients with celiac disease than in healthy individuals, regardless of inflammation status.80
Notably, some of the changes in the gut microbiota of patients with celiac disease cannot be restored after long-term treatment with a gluten-free diet,81 indicating that dysbiosis might be related to a celiac disease-associated genotype. Parmer et al. showed that a mutation in the fucosyltransferase 2 (FUT2) gene, which controls the expression of ABH blood group antigens in mucus and other body secretions,82 is associated with the pathogenesis of celiac disease,83 although the mechanism that underlies this phenomenon has not yet been fully elucidated. Additionally, FUT2 can influence the structure of mucosa-associated bacteria,84 and FUT2 mutations have been shown to lead to reduced bacterial diversity and richness, including a lower abundance of Bifidobacterium spp., in the human gut.85 Decreased abundance of Bifidobacterium spp. is associated with an increased risk for autoimmune diseases,86 and Bifidobacterium spp. are known to protect against Candida albicans colonization. Fut2-null mice display greater susceptibility to C. albicans colonization than wild-type mice,87 and C. albicans infection can trigger the onset of celiac disease.88 Therefore, perturbations of the microbiota due to FUT2 mutation result in lower resistance to colonization by pathobionts, thus contributing to the pathogenesis of celiac disease.
Antibiotic exposure is also a recognized risk factor for the development of celiac disease.89 Perinatal antibiotic treatment (vancomycin) of gluten-sensitive NOD/DQ8 mice worsened gluten-induced pathology90 and led to an overall decrease in fecal microbial diversity. Although the abundance of Proteobacteria, including Escherichia and Helicobacter spp., was enhanced, that of Bacteroides and Parabacteroides spp. was significantly decreased.90 This finding provides additional evidence for the role of the gut microbial community in the development of celiac disease and confirms the relationship between antibiotic use and an increased risk of celiac disease.
Previous epidemiological analyses showed that breastfeeding of infants exerts protective effects against the development of celiac disease. This effect is believed to be mediated by the establishment of specific gut microbiota.91,92 Meta-analysis demonstrated that the risk of later celiac disease was significantly reduced in infants who were breastfed when gluten-containing foods were introduced compared to infants who were not breastfed during this period.92,93 Breastfeeding is known to promote gut colonization by Bifidobacterium spp. However, a recent study has showed that Bifidobacterium spp. are less abundant in the breast milk of mothers with celiac disease, suggesting that infants raised by mothers with celiac disease may have decreased numbers of Bifidobacterium spp.94 This result suggests that breastfeeding may protect infants against the development of celiac disease and that this protective effect is modulated by the microbiota.
It is unclear whether alterations of the microbiota and its components are a cause or a consequence of the development of celiac disease. The fact that both newly diagnosed celiac disease patients as well as those that have been treated with a gluten-free diet have imbalanced microbiotas indicates that the gut microbiota may play a primary role in the pathogenesis of celiac disease. Further research using animal models is needed to elucidate the mechanism by which the microbiota shapes host immune response against gluten (Table 1 and Fig. 1).
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) is a functional bowel disorder that commonly causes abdominal pain, diarrhea, cramping, gas, and constipation.95 A growing number of studies have demonstrated that gut dysbiosis is involved in IBS pathogenesis; specifically gut motility dysfunction, intestinal permeability, and visceral pain responses.96,97 Patients with IBS have greater numbers of Ruminococcaceae and Clostridium cluster XIVa, and lesser numbers of Bacteroides than healthy individuals do.98 It is unclear whether intestinal dysbiosis is the cause of IBS or merely a consequence. The results of animal-based studies support the latter hypothesis. For instance, colonization of germ-free rats with dysbiotic fecal microbiota (e.g., increased Bifidobacteria and decreased Enterobacteriaceae and sulfate-reducing bacteria) isolated from IBS patients was sufficient to cause increased abdominal contractions, a typical symptom of patients with IBS. This observation confirms that the gut dysbiosis present in patients with IBS contributes to disease pathogenesis.99
Patients with IBS also display defects in luminal metabolic function, which is likely caused by dysbiosis. The degree of breath methane production is markedly enhanced in patients with IBS and is correlated with the incidence of constipation. 100 Methane has a negative effect on various aspects of GI motility, including gut transit and contraction. Consistent with the observation of increased methane production, Methanobrevibacter smithii, a predominant methanogen in the human gut,101 was shown to be more abundant in stool samples from patients with constipation-predominant IBS.100 Thus, methanogenic bacteria appear to play a role in the pathogenesis of IBS; however, the factors that promote the bloom of methanogenic bacteria in patients with IBS are not yet known. These findings indicate that microbial imbalance leads to gut dysfunction and contributes to IBS symptoms. Moreover, several meta-analyses have shown that the pathogenesis of IBS is influenced by multiple factors, all of which can result in gut dysbiosis.96 For example, intestinal infections with pathogenic bacteria such as Salmonella, Campylobacter, and Shigella, are known to increase the risk of developing IBS.102 Although enteric infections may directly influence GI motility, infection-induced dysbiosis may also contribute to post-infectious IBS symptoms.103,104 Moreover, epidemiologic studies have shown that the incidence of IBS symptoms is significantly increased in patients who, as children, were treated with antibiotics, particularly macrolides and tetracycline.105,106
In summary, the effects of physical and psychological stressors and dietary factors such as fat consumption, on IBS have been extensively studied.96 However, the precise mechanisms by which these factors influence the gut microbial profile and lead to the development and/or progression of IBS are still unknown. Thus, more research is required to advance our current understanding of the relationship between the intestinal microbiota and gut dysfunction in IBS (Table 1 and Fig. 1).
Mounting evidence suggests that the initiation and development of GI diseases are governed by multiple factors. As described above, current studies indicate that the phenotype associated with commensal bacteria can shift from symbiotic to pathogenic in response to several risk factors. These phenotypic alterations impact the host immune system and the other microorganisms, thereby leading to the development and/or progression of various GI diseases.107 Based on this evidence, therapeutic approaches that aim to correct perturbations of the intestinal bacterial structure and its metabolic function will likely be most effective for the treatment of GI diseases. For example, it has been reported that a diet low in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, and polyols (FODMAPs) reduces GI symptoms in IBS patients by altering the microbial composition and colonic luminal environment, including the pH and SCFA level.108,109
Additionally, healthy fecal microbiota transfer (FMT) appears to be effective for the treatment of IBD.110 In a clinical study, all tested patients with IBD showed resolution of C. difficile symptoms post-FMT.111 In addition, FMT increased bacterial diversity and richness to levels similar to those of healthy donors.112 Similarly, consumption of beneficial microorganisms, called probiotics, has shown great promise as a potential therapeutic approach for the treatment and prevention of CRC.113 Although more clinical trials are clearly needed, the potential role of probiotics in CRC has been evaluated. Administration of Lactobacillus johnsonii modulated immune responses and decreased the risk of pathogen colonization in CRC patients.114 Other studies have demonstrated that the administration of Lactobacillus casei prevented the growth of colorectal tumors in CRC patients for at least 4 years after treatment.115
These trials were limited by the small number of patients included and the short experimental period. Therefore, in the future, larger studies are required to explore the full therapeutic potential of gut microbiota modulation in the treatment of GI diseases.
NOTES
Financial support: This work was supported by a JSPS Postdoctoral Fellowship for Research Abroad (to H. N.-K. and S. K.), the Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America, a Young Investigator Grant from the Global Probiotics Council, and a Michigan Gastrointestinal Research Center pilot feasibility grant (DK034933; to N. K.).
References
1. Kamada N, Seo SU, Chen GY, Núñez G. Role of the gut microbiota in immunity and inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 2013;13:321-335.PMID: 23618829.



2. Kamada N, Núñez G. Regulation of the immune system by the resident intestinal bacteria. Gastroenterology 2014;146:1477-1488.PMID: 24503128.



3. Kamada N, Chen GY, Inohara N, Núñez G. Control of pathogens and pathobionts by the gut microbiota. Nat Immunol 2013;14:685-690.PMID: 23778796.



4. Atarashi K, Tanoue T, Shima T, et al. Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 2011;331:337-341.PMID: 21205640.


5. Lewis SJ, Heaton KW. Increasing butyrate concentration in the distal colon by accelerating intestinal transit. Gut 1997;41:245-251.PMID: 9301506.



6. Furusawa Y, Obata Y, Fukuda S, et al. Commensal microbederived butyrate induces the differentiation of colonic regulatory T cells. Nature 2013;504:446-450.PMID: 24226770.



7. Gérard P. Metabolism of cholesterol and bile acids by the gut microbiota. Pathogens 2013;3:14-24.PMID: 25437605.



8. Mukherjee PK, Sendid B, Hoarau G, Colombel JF, Poulain D, Ghannoum MA. Mycobiota in gastrointestinal diseases. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;12:77-87.PMID: 25385227.



9. Rautava S, Luoto R, Salminen S, Isolauri E. Microbial contact during pregnancy, intestinal colonization and human disease. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:565-576.PMID: 22890113.



10. Ananthakrishnan AN. Epidemiology and risk factors for IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;12:205-217.PMID: 25732745.



11. Manichanh C, Borruel N, Casellas F, Guarner F. The gut microbiota in IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:599-608.PMID: 22907164.



12. Nell S, Suerbaum S, Josenhans C. The impact of the microbiota on the pathogenesis of IBD: lessons from mouse infection models. Nat Rev Microbiol 2010;8:564-577.PMID: 20622892.



13. Frank DN, St Amand AL, Feldman RA, Boedeker EC, Harpaz N, Pace NR. Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial community imbalances in human inflammatory bowel diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2007;104:13780-13785.PMID: 17699621.



14. Henao-Mejia J, Elinav E, Jin C, et al. Inflammasome-mediated dysbiosis regulates progression of NAFLD and obesity. Nature 2012;482:179-185.PMID: 22297845.




15. Wright DP, Rosendale DI, Robertson AM. Prevotella enzymes involved in mucin oligosaccharide degradation and evidence for a small operon of genes expressed during growth on mucin. FEMS Microbiol Lett 2000;190:73-79.PMID: 10981693.



16. Lucke K, Miehlke S, Jacobs E, Schuppler M. Prevalence of Bacteroides and Prevotella spp. in ulcerative colitis. J Med Microbiol 2006;55:617-624.PMID: 16585651.


17. Elinav E, Strowig T, Kau AL, et al. NLRP6 inflammasome regulates colonic microbial ecology and risk for colitis. Cell 2011;145:745-757.PMID: 21565393.



18. Couturier-Maillard A, Secher T, Rehman A, et al. NOD2-mediated dysbiosis predisposes mice to transmissible colitis and colorectal cancer. J Clin Invest 2013;123:700-711.PMID: 23281400.



19. Sellon RK, Tonkonogy S, Schultz M, et al. Resident enteric bacteria are necessary for development of spontaneous colitis and immune system activation in interleukin-10-deficient mice. Infect Immun 1998;66:5224-5231.PMID: 9784526.



20. Sadlack B, Merz H, Schorle H, Schimpl A, Feller AC, Horak I. Ulcerative colitis-like disease in mice with a disrupted interleukin-2 gene. Cell 1993;75:253-261.PMID: 8402910.


21. Kim SC, Tonkonogy SL, Albright CA, et al. Variable phenotypes of enterocolitis in interleukin 10-deficient mice monoassociated with two different commensal bacteria. Gastroenterology 2005;128:891-906.PMID: 15825073.


22. Bohn E, Bechtold O, Zahir N, et al. Host gene expression in the colon of gnotobiotic interleukin-2-deficient mice colonized with commensal colitogenic or noncolitogenic bacterial strains: common patterns and bacteria strain specific signatures. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2006;12:853-862.PMID: 16954804.


23. Kim SC, Tonkonogy SL, Karrasch T, Jobin C, Sartor RB. Dualassociation of gnotobiotic IL-10-/- mice with 2 nonpathogenic commensal bacteria induces aggressive pancolitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2007;13:1457-1466.PMID: 17763473.


24. Rath HC, Wilson KH, Sartor RB. Differential induction of colitis and gastritis in HLA-B27 transgenic rats selectively colonized with Bacteroides vulgatus or Escherichia coli. Infect Immun 1999;67:2969-2974.PMID: 10338507.



25. Brown K, DeCoffe D, Molcan E, Gibson DL. Diet-induced dysbiosis of the intestinal microbiota and the effects on immunity and disease. Nutrients 2012;4:1095-1119.PMID: 23016134.



26. DeVoss J, Diehl L. Murine models of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD): challenges of modeling human disease. Toxicol Pathol 2014;42:99-110.PMID: 24231829.


27. Devkota S, Wang Y, Musch MW, et al. Dietary-fat-induced taurocholic acid promotes pathobiont expansion and colitis in Il10-/- mice. Nature 2012;487:104-108.PMID: 22722865.




28. Muyzer G, Stams AJ. The ecology and biotechnology of sulphate-reducing bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 2008;6:441-454.PMID: 18461075.



29. Rowan F, Docherty NG, Murphy M, Murphy B, Calvin Coffey J, O'Connell PR. Desulfovibrio bacterial species are increased in ulcerative colitis. Dis Colon Rectum 2010;53:1530-1536.PMID: 20940602.


30. Zhang C, Zhang M, Pang X, Zhao Y, Wang L, Zhao L. Structural resilience of the gut microbiota in adult mice under high-fat dietary perturbations. ISME J 2012;6:1848-1857.PMID: 22495068.




31. Hentges DJ, Maier BR, Burton GC, Flynn MA, Tsutakawa RK. Effect of a high-beef diet on the fecal bacterial flora of humans. Cancer Res 1977;37:568-571.PMID: 832279.

32. Palm NW, de Zoete MR, Cullen TW, et al. Immunoglobulin A coating identifies colitogenic bacteria in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 2014;158:1000-1010.PMID: 25171403.



33. Mahid SS, Minor KS, Soto RE, Hornung CA, Galandiuk S. Smoking and inflammatory bowel disease: a meta-analysis. Mayo Clin Proc 2006;81:1462-1471.PMID: 17120402.


34. Cosnes J. Tobacco and IBD: relevance in the understanding of disease mechanisms and clinical practice. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 2004;18:481-496.PMID: 15157822.


35. Morgan XC, Tickle TL, Sokol H, et al. Dysfunction of the intestinal microbiome in inflammatory bowel disease and treatment. Genome Biol 2012;13:R79PMID: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-9-r79. PMID: 23013615.



36. Shaw SY, Blanchard JF, Bernstein CN. Association between the use of antibiotics in the first year of life and pediatric inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2010;105:2687-2692.PMID: 20940708.



37. Kronman MP, Zaoutis TE, Haynes K, Feng R, Coffin SE. Antibiotic exposure and IBD development among children: a population-based cohort study. Pediatrics 2012;130:e794-e803.PMID: 23008454.



38. Mylonaki M, Langmead L, Pantes A, Johnson F, Rampton DS. Enteric infection in relapse of inflammatory bowel disease: importance of microbiological examination of stool. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2004;16:775-778.PMID: 15256979.


39. Schubert AM, Sinani H, Schloss PD. Antibiotic-Induced alterations of the murine gut microbiota and subsequent effects on colonization resistance against Clostridium difficile. MBio 2015;6:e00974-e00915.PMID: 10.1128/mBio.00974-15. PMID: 26173701.




40. Rupnik M, Wilcox MH, Gerding DN. Clostridium difficile infection: new developments in epidemiology and pathogenesis. Nat Rev Microbiol 2009;7:526-536.PMID: 19528959.



41. Musa S, Thomson S, Cowan M, Rahman T. Clostridium difficile infection and inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 2010;45:261-272.PMID: 20025557.


42. Rodemann JF, Dubberke ER, Reske KA, Seo da H, Stone CD. Incidence of Clostridium difficile infection in inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:339-344.PMID: 17368233.


43. Issa M, Vijayapal A, Graham MB, et al. Impact of Clostridium difficile on inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;5:345-351.PMID: 17368234.


44. Cho I, Yamanishi S, Cox L, et al. Antibiotics in early life alter the murine colonic microbiome and adiposity. Nature 2012;488:621-626.PMID: 22914093.




45. Theriot CM, Koenigsknecht MJ, Carlson PE Jr, et al. Antibioticinduced shifts in the mouse gut microbiome and metabolome increase susceptibility to Clostridium difficile infection. Nat Commun 2014;5:3114PMID: 10.1038/ncomms4114. PMID: 24445449.



46. Sorg JA, Sonenshein AL. Bile salts and glycine as cogerminants for Clostridium difficile spores. J Bacteriol 2008;190:2505-2512.PMID: 18245298.



47. Buffie CG, Bucci V, Stein RR, et al. Precision microbiome reconstitution restores bile acid mediated resistance to Clostridium difficile. Nature 2015;517:205-208.PMID: 25337874.



48. Kruis W, Kalek HD, Stellaard F, Paumgartner G. Altered fecal bile acid pattern in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion 1986;35:189-198.PMID: 3817328.


49. Duboc H, Rajca S, Rainteau D, et al. Connecting dysbiosis, bile-acid dysmetabolism and gut inflammation in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 2013;62:531-539.PMID: 22993202.


50. Cao Y, Shen J, Ran ZH. Association between Faecalibacterium prausnitzii reduction and inflammatory bowel disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review of the literature. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2014;2014:872725PMID: 10.1155/2014/872725. PMID: 24799893.




51. Sokol H, Pigneur B, Watterlot L, et al. Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is an anti-inflammatory commensal bacterium identified by gut microbiota analysis of Crohn disease patients. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2008;105:16731-16736.PMID: 18936492.



52. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 2005;55:74-108.PMID: 15761078.


53. Aune D, Chan DS, Lau R, et al. Dietary fibre, whole grains, and risk of colorectal cancer: systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of prospective studies. BMJ 2011;343:d6617PMID: 10.1136/bmj.d6617. PMID: 22074852.



54. Akin H, Tözün N. Diet, microbiota, and colorectal cancer. J Clin Gastroenterol 2014;48(Suppl 1): S67-S69.PMID: 25291132.


55. Oostindjer M, Alexander J, Amdam GV, et al. The role of red and processed meat in colorectal cancer development: a perspective. Meat Sci 2014;97:583-596.PMID: 24769880.


56. Ou J, Carbonero F, Zoetendal EG, et al. Diet, microbiota, and microbial metabolites in colon cancer risk in rural Africans and African Americans. Am J Clin Nutr 2013;98:111-120.PMID: 23719549.




57. Gill CI, Rowland IR. Diet and cancer: assessing the risk. Br J Nutr 2002;88(Suppl 1): S73-S87.PMID: 12215186.


58. Canani RB, Costanzo MD, Leone L, Pedata M, Meli R, Calignano A. Potential beneficial effects of butyrate in intestinal and extraintestinal diseases. World J Gastroenterol 2011;17:1519-1528.PMID: 21472114.



59. Sears CL. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis : a rogue among symbiotes. Clin Microbiol Rev 2009;22:349-369.PMID: 19366918.



60. Rhee KJ, Wu S, Wu X, et al. Induction of persistent colitis by a human commensal, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis, in wild-type C57BL/6 mice. Infect Immun 2009;77:1708-1718.PMID: 19188353.



61. Wu S, Rhee KJ, Albesiano E, et al. A human colonic commensal promotes colon tumorigenesis via activation of T helper type 17 T cell responses. Nat Med 2009;15:1016-1022.PMID: 19701202.




62. Toprak NU, Yagci A, Gulluoglu BM, et al. A possible role of Bacteroides fragilis enterotoxin in the aetiology of colorectal cancer. Clin Microbiol Infect 2006;12:782-786.PMID: 16842574.


63. Cuevas-Ramos G, Petit CR, Marcq I, Boury M, Oswald E, Nougayréde JP. Escherichia coli induces DNA damage in vivo and triggers genomic instability in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2010;107:11537-11542.PMID: 20534522.



64. Arthur JC, Perez-Chanona E, Mühlbauer M, et al. Intestinal inflammation targets cancer-inducing activity of the microbiota. Science 2012;338:120-123.PMID: 22903521.



65. Huxley RR, Ansary-Moghaddam A, Clifton P, Czernichow S, Parr CL, Woodward M. The impact of dietary and lifestyle risk factors on risk of colorectal cancer: a quantitative overview of the epidemiological evidence. Int J Cancer 2009;125:171-180.PMID: 19350627.


66. Vassallo G, Mirijello A, Ferrulli A, et al. Review article: Alcohol and gut microbiota - the possible role of gut microbiota modulation in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2015;41:917-927.PMID: 25809237.


67. Mutlu EA, Gillevet PM, Rangwala H, et al. Colonic microbiome is altered in alcoholism. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2012;302:G966-G978.PMID: 22241860.



68. Yan AW, Fouts DE, Brandl J, et al. Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology 2011;53:96-105.PMID: 21254165.


69. Nistal E, Fernández-Fernández N, Vivas S, Olcoz JL. Factors Determining Colorectal Cancer: The Role of the Intestinal Microbiota. Front Oncol 2015;5:220PMID: 26528432.



70. Mueller S, Saunier K, Hanisch C, et al. Differences in fecal microbiota in different European study populations in relation to age, gender, and country: a cross-sectional study. Appl Environ Microbiol 2006;72:1027-1033.PMID: 16461645.



71. Makivuokko H, Tiihonen K, Tynkkynen S, Paulin L, Rautonen N. The effect of age and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on human intestinal microbiota composition. Br J Nutr 2010;103:227-234.PMID: 19703328.


72. Biagi E, Nylund L, Candela M, et al. Through ageing, and beyond: gut microbiota and inflammatory status in seniors and centenarians. PLoS One 2010;5:e10667PMID: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010667. PMID: 20498852.



73. Marchesi JR, Dutilh BE, Hall N, et al. Towards the human colorectal cancer microbiome. PLoS One 2011;6:e20447PMID: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020447. PMID: 21647227.



74. Kapatral V, Anderson I, Ivanova N, et al. Genome sequence and analysis of the oral bacterium Fusobacterium nucleatum strain ATCC 25586. J Bacteriol 2002;184:2005-2018.PMID: 11889109.



75. Rubinstein MR, Wang X, Liu W, Hao Y, Cai G, Han YW. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes colorectal carcinogenesis by modulating E-cadherin/β-catenin signaling via its FadA adhesin. Cell Host Microbe 2013;14:195-206.PMID: 23954158.



76. Qin J, Li R, Raes J, et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature 2010;464:59-65.PMID: 20203603.




77. Catassi C, Kryszak D, Bhatti B, et al. Natural history of celiac disease autoimmunity in a USA cohort followed since 1974. Ann Med 2010;42:530-538.PMID: 20868314.


78. Cenit MC, Olivares M, Codoñer-Franch P, Sanz Y. Intestinal microbiota and celiac disease: cause, consequence or coevolution? Nutrients 2015;7:6900-6923.PMID: 26287240.



79. Di Cagno R, De Angelis M, De Pasquale I, et al. Duodenal and faecal microbiota of celiac children: molecular, phenotype and metabolome characterization. BMC Microbiol 2011;11:219PMID: 10.1186/1471-2180-11-219. PMID: 21970810.



80. Sánchez E, Donat E, Ribes-Koninckx C, Fernández-Murga ML, Sanz Y. Duodenal-mucosal bacteria associated with celiac disease in children. Appl Environ Microbiol 2013;79:5472-5479.PMID: 23835180.



81. Wacklin P, Laurikka P, Lindfors K, et al. Altered duodenal microbiota composition in celiac disease patients suffering from persistent symptoms on a long-term gluten-free diet. Am J Gastroenterol 2014;109:1933-1941.PMID: 25403367.



83. Parmar AS, Alakulppi N, Paavola-Sakki P, et al. Association study of FUT2 (rs601338) with celiac disease and inflammatory bowel disease in the Finnish population. Tissue Antigens 2012;80:488-493.PMID: 23075394.


84. Tong M, McHardy I, Ruegger P, et al. Reprograming of gut microbiome energy metabolism by the FUT2 Crohns disease risk polymorphism. ISME J 2014;8:2193-2206.PMID: 24781901.




85. Wacklin P, Tuimala J, Nikkilä J, et al. Faecal microbiota composition in adults is associated with the FUT2 gene determining the secretor status. PLoS One 2014;9:e94863PMID: 24733310.



86. Lopez P, Gonzalez-Rodriguez I, Gueimonde M, Margolles A, Suarez A. Immune response to Bifidobacterium bifidum strains support Treg/Th17 plasticity. PLoS One 2011;6:e24776PMID: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024776. PMID: 21966367.



87. Hurd EA, Domino SE. Increased susceptibility of secretor factor gene Fut2-null mice to experimental vaginal candidiasis. Infect Immun 2004;72:4279-4281.PMID: 15213174.



88. Nieuwenhuizen WF, Pieters RH, Knippels LM, Jansen MC, Koppelman SJ. Is Candida albicans a trigger in the onset of coeliac disease? Lancet 2003;361:2152-2154.PMID: 12826451.


89. Mårild K, Ye W, Lebwohl B, et al. Antibiotic exposure and the development of coeliac disease: a nationwide case-control study. BMC Gastroenterol 2013;13:109PMID: 10.1186/1471-230X-13-109. PMID: 23834758.




90. Galipeau HJ, McCarville JL, Huebener S, et al. Intestinal microbiota modulates gluten-induced immunopathology in humanized mice. Am J Pathol 2015;185:2969-2982.PMID: 26456581.



91. Akobeng AK, Ramanan AV, Buchan I, Heller RF. Effect of breast feeding on risk of coeliac disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Arch Dis Child 2006;91:39-43.PMID: 16287899.


92. Peters U, Schneeweiss S, Trautwein EA, Erbersdobler HF. A case-control study of the effect of infant feeding on celiac disease. Ann Nutr Metab 2001;45:135-142.PMID: 11463995.


93. Fälth-Magnusson K, Franzen L, Jansson G, Laurin P, Stenhammar L. Infant feeding history shows distinct differences between Swedish celiac and reference children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 1996;7:1-5.PMID: 8792377.

94. Olivares M, Albrecht S, De Palma G, et al. Human milk composition differs in healthy mothers and mothers with celiac disease. Eur J Nutr 2015;54:119-128.PMID: 24700375.


95. Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, Houghton LA, Mearin F, Spiller RC. Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology 2006;130:1480-1491.PMID: 16678561.


96. Collins SM. A role for the gut microbiota in IBS. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2014;11:497-505.PMID: 24751910.



97. Öhman L, Törnblom H, Simrén M. Crosstalk at the mucosal border: importance of the gut microenvironment in IBS. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2015;12:36-49.PMID: 25446728.



98. Jeffery IB, O'Toole PW, Öhman L, et al. An irritable bowel syndrome subtype defined by species-specific alterations in faecal microbiota. Gut 2012;61:997-1006.PMID: 22180058.


99. Crouzet L, Gaultier E, Del'Homme C, et al. The hypersensitivity to colonic distension of IBS patients can be transferred to rats through their fecal microbiota. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2013;25:e272-e282.PMID: 23433203.


100. Kim G, Deepinder F, Morales W, et al. Methanobrevibacter smithii is the predominant methanogen in patients with constipation-predominant IBS and methane on breath. Dig Dis Sci 2012;57:3213-3218.PMID: 22573345.


101. Dridi B, Raoult D, Drancourt M. Archaea as emerging organisms in complex human microbiomes. Anaerobe 2011;17:56-63.PMID: 21420503.


102. DuPont AW. Postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Infect Dis 2008;46:594-599.PMID: 18205536.



103. Connor BA. Sequelae of traveler's diarrhea: focus on postinfectious irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Infect Dis 2005;41(Suppl 8): S577-S586.PMID: 16267722.



104. Beatty JK, Bhargava A, Buret AG. Post-infectious irritable bowel syndrome: mechanistic insights into chronic disturbances following enteric infection. World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:3976-3985.PMID: 24744587.



105. Mendall MA, Kumar D. Antibiotic use, childhood affluence and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1998;10:59-62.PMID: 9512954.


106. Villarreal AA, Aberger FJ, Benrud R, Gundrum JD. Use of broad-spectrum antibiotics and the development of irritable bowel syndrome. WMJ 2012;111:17-20.PMID: 22533211.

107. Chow J, Tang H, Mazmanian SK. Pathobionts of the gastrointestinal microbiota and inflammatory disease. Curr Opin Immunol 2011;23:473-480.PMID: 21856139.



108. de Roest RH, Dobbs BR, Chapman BA, et al. The low FODMAP diet improves gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with irritable bowel syndrome: a prospective study. Int J Clin Pract 2013;67:895-903.PMID: 23701141.


109. Halmos EP, Christophersen CT, Bird AR, Shepherd SJ, Gibson PR, Muir JG. Diets that differ in their FODMAP content alter the colonic luminal microenvironment. Gut 2015;64:93-100.PMID: 25016597.


110. Borody TJ, Khoruts A. Fecal microbiota transplantation and emerging applications. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2012;9:88-96.PMID: 22183182.


111. van Nood E, Vrieze A, Nieuwdorp M, et al. Duodenal infusion of donor feces for recurrent Clostridium difficile. N Engl J Med 2013;368:407-415.PMID: 23323867.


112. Hourigan SK, Chen LA, Grigoryan Z, et al. Microbiome changes associated with sustained eradication of Clostridium difficile after single faecal microbiota transplantation in children with and without inflammatory bowel disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2015;42:741-752.PMID: 26198180.


113. Kahouli I, Tomaro-Duchesneau C, Prakash S. Probiotics in colorectal cancer (CRC) with emphasis on mechanisms of action and current perspectives. J Med Microbiol 2013;62:1107-1123.PMID: 23558140.


114. Gianotti L, Morelli L, Galbiati F, et al. A randomized doubleblind trial on perioperative administration of probiotics in colorectal cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol 2010;16:167-175.PMID: 20066735.



115. Ishikawa H, Akedo I, Otani T, et al. Randomized trial of dietary fiber and Lactobacillus casei administration for prevention of colorectal tumors. Int J Cancer 2005;116:762-767.PMID: 15828052.


Fig. 1
The pathogenic role of the gut microbiota in gastrointestinal (GI) diseases. Various environmental and immunological factors cause gut dysbiosis. The dysbiotic microbiota exhibits abnormal immune stimulating capacity as well as impaired metabolic functions that lead to development of GI diseases, such as IBD.
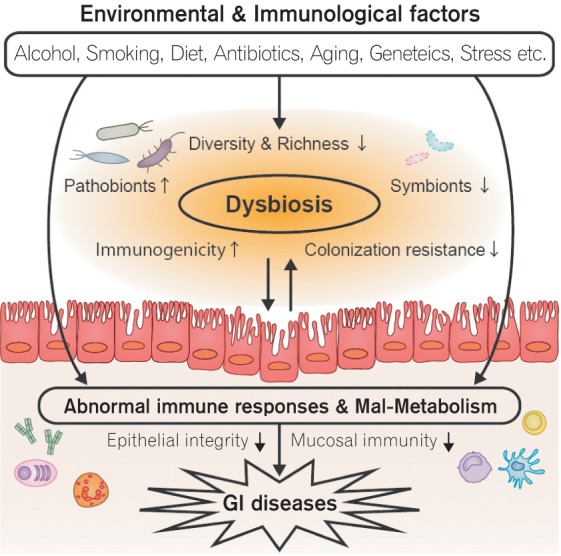
Table 1
Role of Pathogenic Gut Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Diseases
CCL5, Chemokine ligand 5; NIrp, NOD like receptor protein; IL, interleukin; IFN, interIferon; protein; DCA, deoxycholic acid; pks, polyketide synthases; CRC, colorectal cancer; SCFA, short chain fatty acids; LCA, lithocholic acid; ETBF, enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis; STAT3, Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; FUT2, fucosyltransferase 2; spp, species.
| Risk factor | Microbial change | Possible mechanisms | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| IBD | |||
| Genetics (Nlrp6 deficient) | Prevotellaceae ↑, TM7 ↑ | IL-18↓, CCL5↑, and innate and adaptive immune cell recruitment | 14, 15, 16 |
| Genetics (IL-10, IL-2 deficient) | Escherichia coli or Enterococcus faecalis (monocolonization) | IL-12, IFN-γ ↑ | 23 |
| Genetics (HLA-B27) | Bacteroides fragilis (monocolonization) | Unknown | 24 |
| Diet (high fat derived from milk) | Firmicutes ↓, Bilophila wadsworthia ↑ | Immune system (Th1) disruption | 26, 27 |
| Diet (high protein) | Desulfovibrio spp . ↑, Desulfuromonas spp . ↑ | Genotoxic ↑, DNA damage ↑, inflammation ↑ | 28, 29 |
| Diet (high fat, high beef) | Erysipelotrichaceae ↑, Bacteroides fragilis ↑ | Unknown | 30, 31 |
| Smoking | Anaerostipes ↓ | Butyrate ↓ | 35 |
| Antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, metronidazole) | Dorea ↓, Butyricicoccus ↓, Coriobacteriaceae ↓ | Organic acid ↓ (e.g., formic acid, butyrate) | 40, 41 |
| Antibiotics | Clostridium scindens ↓, Clostridium difficile ↑ | DCA ↓ | 47 |
| Unknown | Faecalibacterium prausnitzii ↓ | Anti-inflammatory effect ↓ | 50, 51 |
| Unknown | pks+ Escherichia coli ↑ | Colibactin ↑, DNA damage ↑ | 64 |
| CRC | |||
| Diet (high fat, low fiber) | Butyrate-producing bacteria ↓, hydrogen sulfide-producing bacteria ↑ | SCFAs ↓ (e.g., acetate, butyrate, propionate), secondary bile acids ↑ (e.g., LCA, DCA) | 56, 57, 58 |
| Diet (high beef) | Bacteroides fragilis (ETBF) ↑ | Wnt/β-catenin signaling ↑ IL-17-driven STAT3 ↑ | 31, 59, 60, 61, 62 |
| Alcohol | Erysipelotrichaceae ↑ | Unknown | 68, 69 |
| Aging | Faecalibacterium prausnitzii ↓, Roseburia intestinalis ↓ | Butyrate ↓, anti-inflammatory property ↓ | 72, 73 |
| Unknown | pks+ Escherichia coli ↑ | Colibactin ↑, DNA damage ↑ | 64 |
| Unknown | Fusobacterium nucleatum ↑ | E-cadherin/β-catenin signaling ↑ | 75, 76 |
| Celiac disease | |||
| Genetics (FUT2 mutation) | Bifidobacterium spp. ↓, Candida albicans ↑ | Unknown | 85, 87, 88 |
| Antibiotic (Vancomycin) | Bacteroides ↓, Parabacteroides ↓, Escherichia ↑, Helicobacter ↑ | Unknown | 90 |
| Breastfeeding (by mother with celiac disease) | Bifidobacterium spp. ↓ | Unknown | 92, 93, 94 |
| IBS | |||
| Infection | Salmonella ↑, Campylobacter ↑, Shigella ↑ | Unknown | 102 |
| Unknown | Methanobrevibacter smithii ↑ | Methane-driven gut dysfunction | 100, 101 |
- TOOLS






